Why Are Printing Circuit Boards Essential for Modern Electronics
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern electronics, printing circuit boards (PCBs) stand out as indispensable components that enable the functionality of a myriad of devices. From smartphones to medical instruments, the intricate designs of printing circuit boards serve as the backbone, facilitating the electrical connections that power our everyday technology. These boards not only provide structural support for electronic components but also ensure effective communication between them, making them crucial for the seamless operation of complex systems.
As technology advances, the demand for more sophisticated and compact electronics has surged, emphasizing the need for innovative printing circuit boards. The evolution of PCB manufacturing techniques has led to the development of multi-layer, flexible, and even biodegradable boards, showcasing how this field adapts to the requirements of modern society. Furthermore, the miniaturization of devices necessitates the precise engineering of printing circuit boards, ensuring that they can accommodate powerful electronics in increasingly smaller footprints. Thus, understanding the significance of printing circuit boards is essential for grasping the broader narrative of technological progress and its impact on our daily lives.
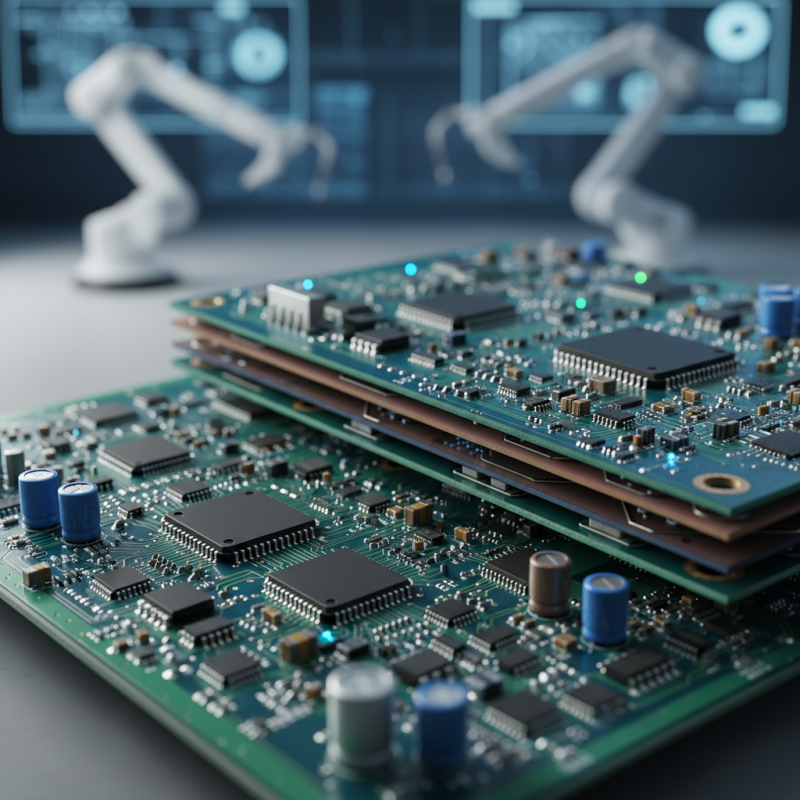
Understanding the Functionality of Printed Circuit Boards in Electronics
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) play a pivotal role in modern electronics by serving as the foundational platform that connects and supports various electronic components. At their core, PCBs provide a structured layout that organizes the connections between components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits. This organization not only facilitates electrical interconnections but also enhances the reliability and durability of electronic devices. By reducing the complexity of wiring and ensuring that components are securely mounted, PCBs allow for sophisticated designs that are compact and efficient.
Moreover, the functionality of printed circuit boards extends beyond mere connectivity. They enable the controlled flow of electricity through carefully designed pathways, which can be tailored to meet specific performance requirements. This adaptability is crucial in applications ranging from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. With advancements in PCB technology, including multi-layer boards and flexible designs, engineers can create intricate circuits that are capable of performing complex tasks while occupying minimal space. The evolution of PCBs has therefore been instrumental in driving innovation across various fields, making them indispensable in the realm of modern electronics.
The Evolution of Printed Circuit Board Technology and Its Impact
The evolution of printed circuit board (PCB) technology has dramatically reshaped the landscape of modern electronics.
Initially, PCBs were simple, single-layer designs primarily used for basic electronics. Over the decades, the technology has advanced, introducing multi-layer boards, flexible circuits, and high-density interconnects (HDI). This evolution has allowed for the miniaturization of electronics and increased functionality, enabling devices to become more compact and efficient than ever before. The shift towards automated manufacturing has also improved production speeds and reduced costs, making sophisticated electronics accessible to a broader audience.
Tip: When considering PCB design, prioritizing the layout can greatly impact performance. Proper placement of components and routing of traces can minimize signal interference and improve overall reliability.
As PCBs continue to evolve, new technologies such as embedded components and advanced materials are driving further innovation. For instance, the introduction of materials that can withstand higher temperatures and increased electrical demands opens the door to applications in industries such as automotive and aerospace. Consequently, these advancements not only enhance the capabilities of electronics but also promote sustainability by enabling more energy-efficient designs.
Tip: Keep abreast of the latest PCB material advancements to ensure your designs are future-proof and able to leverage emerging technologies.
Key Materials Used in Manufacturing Printed Circuit Boards

The manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs) is crucial for the backbone of modern electronics. The industry heavily relies on a variety of key materials that ensure the reliability and functionality of these boards. Among the primary materials used are substrates like FR-4, which is a composite material consisting of woven glass fiber and epoxy resin. Its excellent insulating properties along with mechanical strength make it a preferred choice. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global PCB substrate market is projected to reach $17.4 billion by 2026, underscoring the rising demand for efficient and durable substrates.
In addition to substrates, conductive layers play an essential role in PCB fabrication. Copper remains the most widely used metal due to its superior electrical conductivity. A recent market analysis revealed that the global copper PCB market size is expected to witness significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for electronics in sectors such as telecommunications and automotive. Furthermore, solder mask and silk screen inks are additional materials that enhance functionality and aesthetic appeal, providing protection and allowing easy identification of PCB layout features. Understanding these key materials helps elucidate why PCBs are foundational to the operation and reliability of modern electronic devices.
Design Considerations for Effective Circuit Board Layouts
When designing effective circuit board layouts, several key considerations must be taken into account to ensure reliability and performance. First, the arrangement of components on the board is crucial. Designers should prioritize a layout that minimizes the length of signal paths while avoiding sharp angles, which can lead to signal degradation. The placement of high-frequency components should take into consideration their proximity to other elements, particularly ground planes, to help reduce electromagnetic interference. Additionally, it is vital to distribute heat-generating components evenly across the board to facilitate better thermal management and prevent hotspots.
Another critical aspect of circuit board design is the importance of proper grounding and power distribution. Effective grounding techniques can significantly improve the overall performance of the circuit by reducing noise and enhancing signal integrity. Designers often use multiple ground planes to create a low-impedance return path, which is essential for high-speed applications. Furthermore, ensuring that power distribution is well thought out helps to maintain voltage levels and prevent fluctuations that could impair functionality. Balancing these design considerations is essential for creating circuit boards that meet the demands of modern electronics, promoting efficiency and longevity in device performance.
Why Are Printing Circuit Boards Essential for Modern Electronics - Design Considerations for Effective Circuit Board Layouts
| Design Consideration | Importance | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Layer Stack-up | Determines signal integrity and electromagnetic interference | Use a balanced layer stack-up to minimize distortion |
| Trace Width | Affects current carrying capacity and resistance | Calculate width based on current requirements and thickness |
| Via Type | Influences signal propagation and performance | Select appropriate via type for specific applications |
| Component Placement | Affects assembly ease and electromagnetic performance | Group related components and minimize trace lengths |
| Grounding Strategy | Critical for reducing noise and improving performance | Implement a solid ground plane and star grounding |
The Role of Printed Circuit Boards in Electronic Device Performance
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) play a vital role in the performance of electronic devices, acting as the backbone that interconnects various components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global PCB market is projected to reach $85 billion by 2026, highlighting the increasing reliance on these essential components in modern electronics. PCBs facilitate efficient signal transmission and ensure stable electrical connections, ultimately influencing the overall functionality and reliability of devices.
Moreover, the design and manufacturing quality of PCBs directly impact the performance metrics of electronic products. As electronic devices become more complex and compact, the need for high-density interconnections has surged. A study from IPC — Association Connecting Electronics Industries points out that over 25% of failures in electronic devices can be traced back to PCB-related issues. This emphasizes the importance of advanced PCB technologies, such as multilayer designs and high-frequency materials, which enhance the speed and performance of today’s electronics. The ongoing advancements in PCB fabrication techniques are essential for accommodating the ever-evolving demands of consumer electronics, telecommunications, and automotive applications.
Related Posts
-
Understanding the Role of PCB Boards in the Growth of the Global Electronics Market
-

How to Choose the Best PCB Board for Your Electronic Projects
-
Best PCB Electronics: A Comprehensive Comparison of Top Choices for Your Projects
-
Navigating the 2025 PCB Design and Assembly Trends for Global Buyers
-
Navigating Import Export Certifications for the Best Circuit Board Procurement Strategies
-
Understanding the Essentials of PCB Design and Assembly for Beginners
MSIRobot