What is Flex PCB and How Does it Impact Modern Electronics Design
In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern electronics design, the Flex PCB (Flexible Printed Circuit Board) has emerged as a pivotal innovation. Renowned expert Dr. Emily Chen, a leading figure in flexible electronics, asserts, “Flex PCBs are revolutionizing the way we approach circuit design, enabling unprecedented flexibility and compactness.” This adaptability allows engineers to create intricate designs that were once deemed impossible, making Flex PCBs a cornerstone in various applications, from medical devices to consumer electronics.
The unique properties of Flex PCBs facilitate streamlined manufacturing processes and enhance the performance of electronic devices. Unlike traditional rigid boards, Flex PCBs can bend and fold, providing significant advantages in space-constrained environments. This characteristic not only aids in reducing the overall size of devices but also contributes to improved reliability and durability, crucial factors in sectors where performance is paramount.
As industries continue to push the boundaries of what is achievable in design and functionality, the role of Flex PCBs becomes increasingly indispensable. Their ability to integrate seamlessly into modern devices heralds a new era in electronics design, challenging engineers to think innovatively and leverage the full potential of this technology.
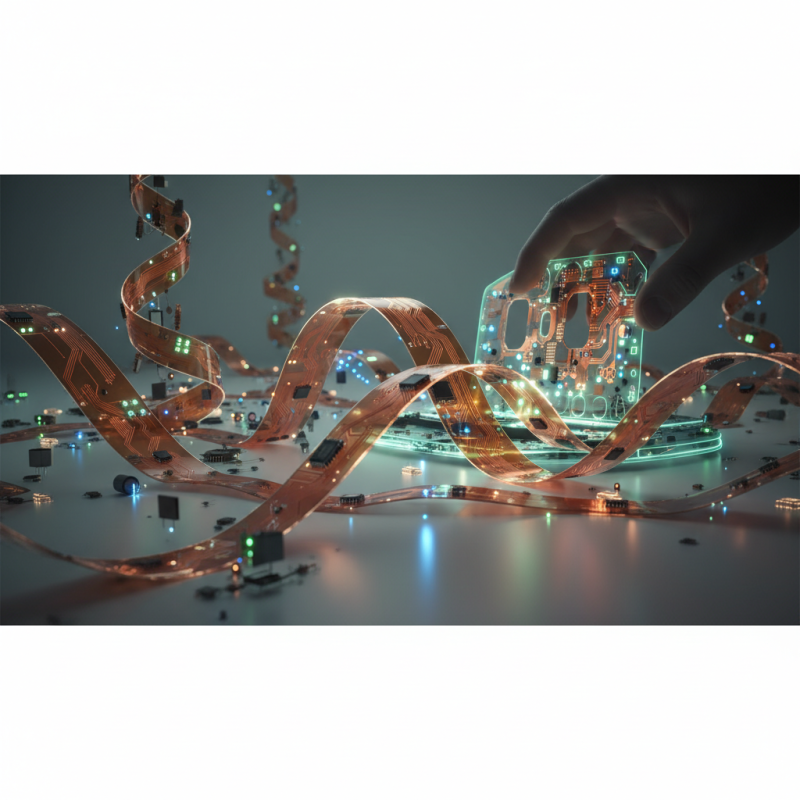

What is a Flexible Printed Circuit Board (Flex PCB)?
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (Flex PCBs) are a vital innovation in modern electronics design, offering significant advantages over traditional rigid circuit boards. These flexible circuits are made from materials that can bend, twist, and fold, allowing for the creation of compact and lightweight designs. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global flex PCB market is projected to reach $38.71 billion by 2026, driven by the growing demand in various sectors including consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices.
Flex PCBs enable intricate layouts that can fit seamlessly into tight spaces, a feature that has become increasingly essential in the era of miniaturization. They provide higher reliability, as their malleable design helps to reduce the risk of solder joint failures that are common in rigid boards, especially in dynamic environments. Moreover, flexible circuits can save assembly costs as they can often be integrated into other components, minimizing the need for additional connectors and interconnections.
Tip: When designing with Flex PCBs, consider the mechanical stresses your application may face. Ensure that you understand the bending radii specifications and use appropriate materials to enhance the board's durability and performance.
Another critical advantage is the ability to create 3D assemblies that can enhance device functionality without increasing size. The lightweight nature of flex circuits also contributes to more energy-efficient designs, which is crucial as electronics strive for sustainability. Research published in the Journal of Electronics Manufacturing highlights that the adoption of flexible circuitry can lead to a reduction in component weight by up to 50%, significantly impacting overall product design.
Tip: Always collaborate closely with your PCB manufacturer to optimize the design for minuscule features and ensure proper signal integrity, especially when working with high-frequency applications.
What is Flex PCB and How Does it Impact Modern Electronics Design
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A flexible printed circuit board that can be bent and folded. | Enables compact designs. |
| Material | Typically made from polyimide or polyester film. | High thermal stability and flexibility. |
| Applications | Used in smartphones, cameras, and medical devices. | Ideal for space-restricted applications. |
| Manufacturing Process | Involves etching, layering, and lamination of flexible substrates. | Allows for complex designs with reduced weight and size. |
| Advantages | Lightweight, flexible, and can be integrated into a 3D space. | Reduces assembly time and improves reliability. |
| Challenges | More expensive than traditional PCBs and requires specialized manufacturing equipment. | Requires careful design consideration. |
The Manufacturing Process of Flex PCBs: Key Steps and Technologies

The manufacturing process of Flex PCBs involves several critical steps that ensure the creation of high-quality, flexible circuit boards tailored for modern electronics. Initially, the design phase is paramount, where innovative layouts are crafted using advanced software that accommodates the unique characteristics of flexible substrates. This includes defining the circuit paths and ensuring that components can be mounted effectively on a non-rigid surface. Once the design is finalized, the next step is material selection, where flexible substrates such as polyimide or polyester are chosen for their durability and electrical properties.
Following material selection, the production process moves into the fabrication stage, which typically includes the application of conductive materials through techniques such as screen printing or photolithography. These methods allow for precise deposition of copper traces on the substrate, followed by etching to remove excess material and create the desired circuit patterns. After fabrication, the boards undergo testing to evaluate their electrical performance and ensure they meet design specifications. The entire manufacturing process emphasizes precision and quality control, as the unique properties of Flex PCBs require careful handling and execution to deliver reliable and efficient products for a variety of applications in modern electronics.
Applications of Flex PCBs in Modern Electronics: Trends and Innovations
Flexible printed circuit boards (Flex PCBs) are rapidly gaining traction in modern electronics design due to their versatility and compactness. According to a recent report by the Flexible Printed Circuit Association, the global market for flexible PCBs is expected to reach approximately $28 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 10.8%. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for miniaturized electronic devices in sectors such as consumer electronics, automotive, and medical equipment. The unique ability of Flex PCBs to bend and conform to specific shapes allows for innovative designs that enhance device functionality and reduce assembly costs.
In applications ranging from smartphones to wearables, Flex PCBs are enabling significant trends in electronics design. For instance, the integration of flexible circuits in wearable medical devices has improved both patient comfort and device performance. Research indicates that nearly 60% of new medical devices launched in recent years incorporate some form of flexible electronics. Additionally, the automotive industry is leveraging Flex PCBs to reduce weight and improve space efficiency, leading to advancements in electric vehicles where weight reduction is critical for battery performance. As technologies continue to evolve, the adaptability of Flex PCBs will play a crucial role in pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in modern electronics design.
Advantages of Flex PCBs Over Traditional Rigid PCBs: A Comparative Analysis
Flexible PCBs (Flex PCBs) have gained significant traction in modern electronics design, offering distinct advantages over traditional rigid PCBs. One of the most notable benefits is their ability to bend and conform to complex shapes, resulting in designs that can fit into tighter spaces. This is particularly useful in the miniaturization of devices where traditional rigid boards would be impractical. The reduced weight and thickness of Flex PCBs also contribute to more efficient and compact electronic devices, making them ideal for applications in wearable technology and mobile devices.
Another key advantage of Flex PCBs is their enhanced durability. Unlike rigid PCBs that can break or fracture under stress, Flex PCBs are designed to withstand high flexural stress and vibration, making them more reliable in dynamic environments. This flexibility not only enhances the lifespan of the components but also facilitates easier assembly processes, as they can be layered or stacked in various configurations without the concern of damaging the board. Additionally, Flex PCBs often come with improved thermal performance, allowing for better heat dissipation which is crucial for high-performance electronics.
Future Trends in Flex PCB Technology and Its Impact on Electronics Design
Flex PCBs, or flexible printed circuit boards, have emerged as a transformative technology in modern electronics design. As the demand for compact, lightweight, and high-performance devices continues to grow, the role of Flex PCBs in allowing for greater design flexibility and space efficiency cannot be overstated. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global flexible printed circuit board market is projected to reach $30 billion by 2026, showcasing an annual growth rate of over 10%. This trend reflects the increasing integration of Flex PCBs in industries ranging from consumer electronics to medical devices.
Future trends in Flex PCB technology indicate a shift towards enhanced functionality, with the incorporation of advanced materials and manufacturing processes. As engineers aim for more intricate designs with improved thermal management, the adoption of innovative substrates, such as polyimide and even printed electronics, is on the rise. This evolution not only enhances device performance but also reduces the overall footprint, which is critical for modern applications like wearables and IoT devices. Moreover, industry analysts suggest that the growing emphasis on miniaturization will further propel the adoption of Flex PCBs, setting new benchmarks in circuitry design.
Tips: When designing with Flex PCBs, consider the bending radius and ensure that components are adequately spaced to avoid stress points. Additionally, integrating solder mask and surface finish options can enhance durability and reliability, particularly for devices subjected to frequent movement. Always consult with manufacturers for material compatibility to ensure optimal performance in your specific application.
Impact of Flex PCB Technology on Modern Electronics Design
This chart illustrates the various impacts of Flex PCB technology on electronics design, rated on a scale from 1 to 10. Notably, design flexibility scores the highest, highlighting its importance in modern electronics.
Related Posts
-

Unlocking the Future of Electronics with the Best Flex PCB Assembly Solutions
-
How to Optimize Your Flexible Printed Circuit Board Production for Maximum Efficiency and Cost Savings
-
How to Navigate the Process of Flex PCB Assembly for Your Projects
-
Understanding the Future of Electronics through Flex Circuit Board Innovations
-
2025 Guide: How to Optimize Your Flex PCB Assembly Process for Maximum Efficiency
-

How to Choose the Best PCB Board for Your Electronic Projects
MSIRobot